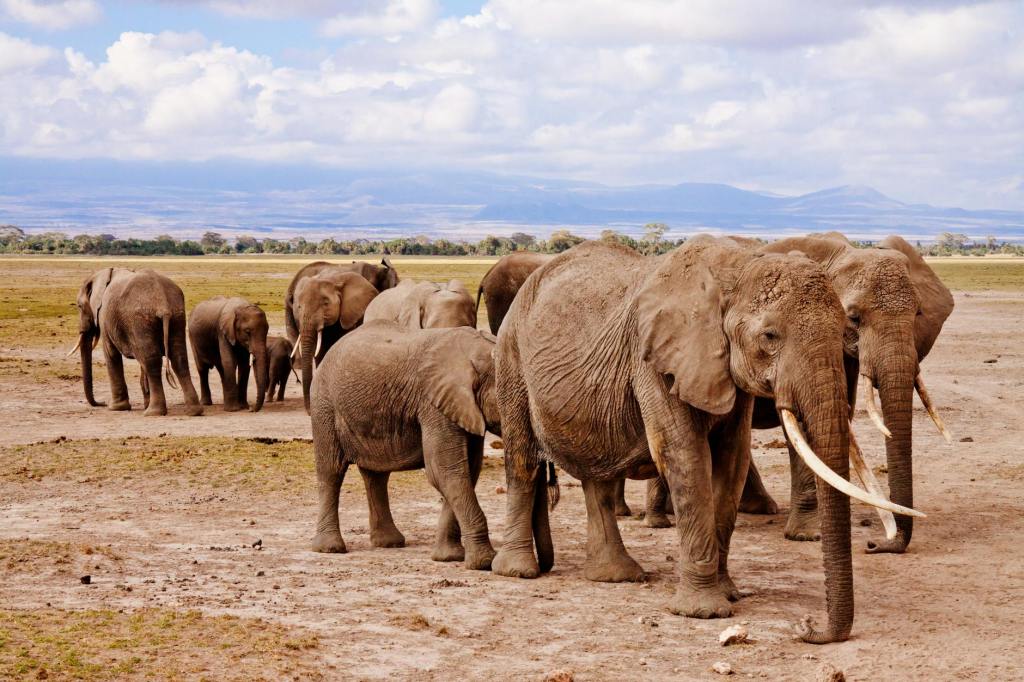
- Unique Foot Structure: Elephants have a flexible foot with a fatty, cushioned pad that acts like a shock absorber, allowing them to move quietly despite their massive size. This pad expands under pressure and contracts when lifted, adapting to different terrains.
- Teeth Replacement Cycle: Elephants grow six sets of molar teeth throughout their lives. As one set wears down, another pushes forward to replace it, a process that continues until old age when they may struggle to chew tough vegetation.
- Infrasound Communication: Elephants use low-frequency infrasound, below human hearing range, to communicate over distances up to 6 miles (10 km). These rumbles can convey complex messages like warnings or mating calls.
- Trunk Muscle Count: An elephant’s trunk contains about 40,000 muscles (no bones), giving it incredible dexterity to pick up objects as small as a peanut or as heavy as 700 pounds (315 kg).
- Memory Through Smell: Elephants rely heavily on their sense of smell, which is so acute they can detect water sources up to 12 miles (19 km) away and recognize individual elephants by scent alone.
- Ear Cooling Mechanism: African elephants flap their large ears to cool down, as the thin skin and dense blood vessels help dissipate heat. The ears’ unique vein patterns are as distinctive as human fingerprints.
- Self-Medication Behavior: Elephants practice zoopharmacognosy, intentionally eating specific plants or soil (like kaolin clay) to treat ailments such as digestive issues or to induce labor in pregnant females.
- Social Grief Rituals: Elephants exhibit mourning behaviors, gently touching or covering dead relatives’ bones with dirt or leaves. They may revisit these sites, suggesting emotional memory.
- Musth Aggression Phase: Male elephants undergo a periodic state called musth, marked by a surge in testosterone, leading to aggressive behavior and a tar-like secretion from temporal glands. It can last weeks to months.
- Diverse Diet Adaptability: While known for eating grasses and leaves, elephants can consume over 300 plant species, including unconventional foods like fermented fruit, which can lead to rare instances of intoxication.




For more information check out these two sites:
- World Wildlife Fund (WWF) – Elephant Species Page
- Link: www.worldwildlife.org/species/elephant
- WWF is a globally recognized conservation organization that conducts direct research and fieldwork on wildlife, including elephants. This page provides detailed information on elephant species, threats like poaching and habitat loss, and conservation efforts.
- Elephants Without Borders – Elephant Research
- Link: elephantswithoutborders.org/research/
- Elephants Without Borders is a research organization focused on elephant conservation, conducting primary studies such as tracking elephant movements and analyzing DNA from dung samples. They conduct research, like monitoring home ranges in Botswana.














Thank you for taking the time to share your thoughts. Your voice is important to us, and we truly value your input. Whether you have a question, a suggestion, or simply want to share your perspective, we’re excited to hear from you. Let’s keep the conversation going and work together to make a positive impact on our community. Looking forward to your comments!